Live Table Add Edit Delete MySQL Data in Node.js" is a popular feature of web applications that allows users to manipulate data on a page without having to refresh the page. This feature can be implemented using Node.js and MySQL, and in this article, we will walk through a step-by-step guide on how to create a live table that can add, edit and delete data using Node.js and MySQL.
To get started, we need to create a Node.js project and install the required dependencies. We can do this by running the following commands:
mkdir live_table_insert_update_delete
cd live_table_insert_update_delete
npm init -y
npm install express mysql body-parser
The above commands will create a new directory called live_table_insert_update_delete, initialize a new Node.js project and install the required dependencies.
Next, we need to create a MySQL database and table that we will use to store our sample data. We can do this by running the following SQL commands:
CREATE DATABASE testing;
USE testing;
CREATE TABLE sample_data (
id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
first_name varchar(255) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(255) NOT NULL,
age int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
The above commands will create a new database called testing and a table called sample_data with four columns: id, first_name, last_name, and age.
Now we have create a new file called server.js and add the following code:
server.js
//imports the Express framework
const express = require('express');
//import mysql module
const mysql = require('mysql');
//import body-parser module
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
//creates an instance of the Express application
const app = express();
// Add middleware for parse incoming request body
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended : false }));
// Add middleware for parse incoming data in JSON
app.use(bodyParser.json());
//Make MySQL Database Connection
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host : 'localhost',
database : 'testing',
user : 'root',
password : ''
});
//Check MySQL Database Connection
connection.connect((error) => {
console.log('MySQL Database is connected Successfully');
});
//Create Route for Load index.html file
app.get("/", (request, response) => {
response.sendFile(__dirname + "/index.html");
});
//Crate Route handle get request
app.get("/get_data", (request, response) => {
const sql = `SELECT * FROM sample_data ORDER BY id ASC`;
connection.query(sql, (error, results) => {
console.log(error);
response.send(results);
});
});
//Create Route for Insert Data Operation
app.post("/add_data", (request, response) => {
const first_name = request.body.first_name;
const last_name = request.body.last_name;
const age = request.body.age;
const sql = `
INSERT INTO sample_data
(first_name, last_name, age)
VALUES ("${first_name}", "${last_name}", "${age}")
`;
connection.query(sql, (error, results) => {
response.json({
message : 'Data Added'
});
});
});
//Create Route for Update Data Operation
app.post('/update_data', (request, response) => {
const variable_name = request.body.variable_name;
const variable_value = request.body.variable_value;
const id = request.body.id;
const sql = `UPDATE sample_data SET `+variable_name+`= "${variable_value}" WHERE id = "${id}"`;
connection.query(sql, (error, results) => {
response.json({
message : 'Data Updated'
});
});
});
//Create Route for Delete data operation
app.post("/delete_data", (request, response) => {
const id = request.body.id;
const sql = `DELETE FROM sample_data WHERE id = '${id}'`;
connection.query(sql, (error, results) => {
response.json({
message : 'Data Deleted'
});
});
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server listening on port 3000');
});
This is a Node.js server-side code that creates a web application using the Express framework, and connects to a MySQL database to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations. Here is a brief description of the code:
- Import the required modules: Express, MySQL, and body-parser.
- Create an instance of the Express application.
- Add middleware for parsing incoming request body, including JSON data.
- Create a MySQL database connection and check if it is connected successfully.
- Create a route to serve the index.html file.
- Create a route to handle GET requests and retrieve data from the MySQL database.
- Create a route to handle POST requests and insert data into the MySQL database.
- Create a route to handle POST requests and update data in the MySQL database.
- Create a route to handle POST requests and delete data in the MySQL database.
- Listen to the server on port 3000.
Overall, this code provides the backend functionality to serve a web application and perform CRUD operations on a MySQL database.
After this, we have to create index.html file for write HTML code and Vanilla JavaScript code.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Live Table Insert Update Delete in Node.js with MySQL</title>
<link href="https://getbootstrap.com/docs/5.1/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-1BmE4kWBq78iYhFldvKuhfTAU6auU8tT94WrHftjDbrCEXSU1oBoqyl2QvZ6jIW3" crossorigin="anonymous">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5 mb-5">
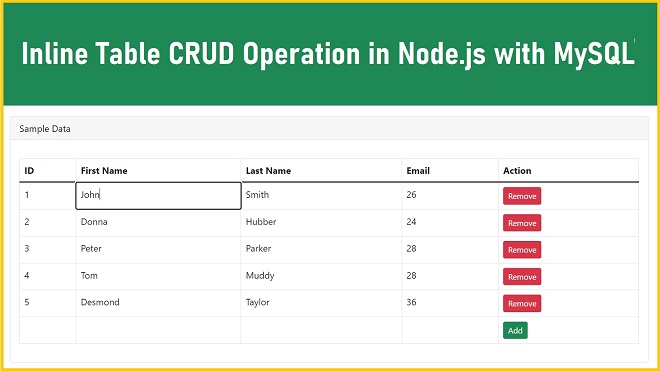
<h1 class="text-danger text-center"><b>Inline Table CRUD Operation in Node.js with MySQL - Delete Data</b></h1>
<div class="mt-3 mb-3">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">Sample Data</div>
<div class="card-body">
<table class="table table-bordered mt-3">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody id="results">
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script>
const results_body = document.querySelector('#results');
load_data();
function load_data()
{
const request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open(`get`, `/get_data`);
let html = '';
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
if(request.readyState === XMLHttpRequest.DONE && request.status === 200)
{
const results = JSON.parse(request.responseText);
results.forEach(result => {
html += `
<tr>
<td>`+result.id+`</td>
<td contenteditable onblur="update_data(this, 'first_name', '`+result.id+`')">`+result.first_name+`</td>
<td contenteditable onblur="update_data(this, 'last_name', '`+result.id+`')">`+result.last_name+`</td>
<td contenteditable onblur="update_data(this, 'age', '`+result.id+`')">`+result.age+`</td>
<td><button type="button" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm" onclick="delete_data(`+result.id+`)">Remove</button></td>
</tr>
`;
});
html += `
<tr>
<td></td>
<td contenteditable id="first_name_data"></td>
<td contenteditable id="last_name_data"></td>
<td contenteditable id="age_data"></td>
<td><button type="button" class="btn btn-success btn-sm" onclick="add_data()">Add</button></td>
</tr>
`;
results_body.innerHTML = html;
}
};
request.send();
}
function add_data()
{
const first_name = document.getElementById('first_name_data');
const last_name = document.getElementById('last_name_data');
const age = document.getElementById('age_data');
const param = `first_name=`+first_name.innerText+`&last_name=`+last_name.innerText+`&age=`+age.innerText+``;
const request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open(`POST`, `/add_data`, true);
request.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
if(request.readyState === XMLHttpRequest.DONE && request.status === 200)
{
alert("Data Added");
load_data();
}
};
request.send(param);
}
function update_data(element, variable_name, id)
{
const param = `variable_name=`+variable_name+`&variable_value=`+element.innerText+`&id=`+id+``;
const request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open(`POST`, `/update_data`, true);
//Send the proper header information along with the request
request.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
if(request.readyState === XMLHttpRequest.DONE && request.status === 200)
{
alert('Data Updated');
}
};
request.send(param);
}
function delete_data(id)
{
if(confirm("Are you sure you want to remove it?"))
{
const param = `id=`+id+``;
const request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open('POST', `/delete_data`, true);
request.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
request.onreadystatechange = () => {
if(request.readyState === XMLHttpRequest.DONE && request.status === 200)
{
alert('Data Deleted');
load_data();
}
};
request.send(param);
}
}
</script>
This code is a web page with a table that performs CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in Node.js with MySQL. The table is displayed in a Bootstrap card, and it shows a list of people with their IDs, first and last names, email, and gender. The table can be edited inline, and it has an "Add" button that adds a new row to the table, a "Remove" button that deletes a row from the table, and an "Update" button that updates the data in the table.
The JavaScript code uses XMLHttpRequest to send asynchronous HTTP requests to the server-side Node.js application, which interacts with a MySQL database to perform the CRUD operations. The load_data() function sends a GET request to the server-side application to retrieve the data and displays it in the table using HTML. The add_data(), update_data() and delete_data() functions send POST requests to the server-side application to perform the corresponding operations.
In conclusion, the Live Table Add Edit Delete MySQL Data in Node.js is a web application that allows users to perform basic CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations on a MySQL database using Node.js. The application uses an HTML table to display the data from the database, which can be edited, updated, and deleted in real-time. The code uses AJAX requests to communicate with the server-side Node.js application, which handles the database operations. This application can be useful for developers who want to learn how to build a basic CRUD application using Node.js and MySQL or for those who need a simple way to manage data stored in a MySQL database.



Social Header
Laporkan Penyalahgunaan
How to Merge Arrays in Node.js
Simplifying User Authentication with JWT Tokens in Node.js
Display Dynamic MySQL Data in Bootstrap 5 Offcanvas Using Node.js: A Step-by-Step Guide
Cari Blog Ini